
Your goal should be to maintain a balance between offering credit to drive sales and protecting your cash flow that aligns with industry norms. Creating a table for this schedule also makes it easy to compare the total amount outstanding in each aging category while offering quick insights into the status of each customer account. Learn how to use an AR Aging Report to manage outstanding invoices, improve cash flow, and strengthen customer relationships with practical strategies.

Accounts receivable aging
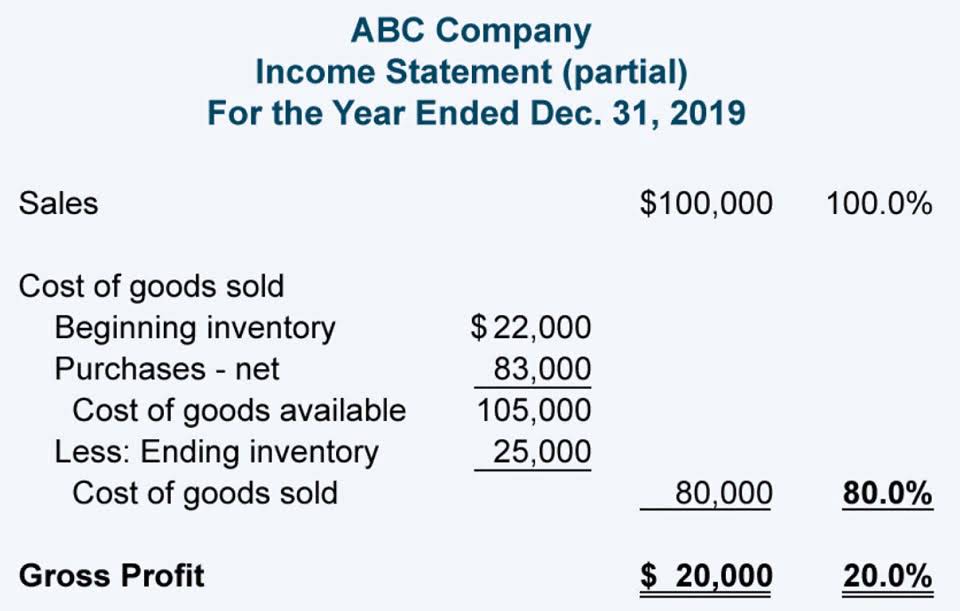
Under the Aging of Accounts Receivable Method for accounting for bad debts, a company creates an estimate of bad debts based on the age of outstanding invoices. This estimate is based on a company’s Aging of Accounts Receivable report. An Accounts Receivable Aging Report separates outstanding invoices into columns based on the age of the invoices.
- Some business owners will even start mentioning the possibility of sending the amount to collections at this point.
- If the average age of accounts receivables is large, its ability to recover credit sales is worse.
- If a company experiences difficulty collecting what it’s owed, for example, it may elect to extend business on a cash-only basis to serial late payers.
- As you organize invoices into the different aging buckets (0-30 days, days, etc.), you’re essentially categorizing them by how long they’ve been outstanding.
- For instance, if payment was due on January 15th, and it’s now January 25th, you would mark it as being 10 days past due.
- The sum of the estimated amounts for all categories yields the total estimated amount uncollectible and is the desired credit balance (the target) in the Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts.
Formula for Calculating Bad Debt Expense
- With this method, accounts receivable is organized into categories by length of time outstanding, and an uncollectible percentage is assigned to each category.
- The bad debt expense required is recorded with the following aging of accounts receivable method journal entry.
- The first entry reverses the bad debt write-off by increasing Accounts Receivable (debit) and decreasing Bad Debt Expense (credit) for the amount recovered.
- You currently use the income statement method to estimate bad debt at 4.5% of credit sales.
- Decisions regarding provisions and write offs are taken based on this report.
By tracking your accounts receivable aging, you can pinpoint how much is owed to your business and for how long. The aging of receivables method is an accounting practice that categorizes a company’s unpaid customer invoices based on how long they have been outstanding. Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) tells you the average number of days it takes to collect payments after a sale. Cash Flow Management for Small Businesses A lower DSO generally means you’re collecting payments quickly, which is good for your cash flow.
How to Use an Accounts Receivable Aging Report

The percentage of receivables method estimates the allowance for doubtful accounts using a percentage of the accounts receivable at the end of the accounting period. The information in an aging schedule also is useful to management for other purposes. Analysis of aging of receivables method collection patterns of accounts receivable may suggest the need for changes in credit policies or for added financing. For example, if the age of many customer balances has increased to days past due, collection efforts may have to be strengthened. Or, the company may have to find other sources of cash to pay its debts within the discount period.
- The percentage of credit sales method directly estimates the bad debt expense and records this as an expense in the income statement.
- Your accounts receivable aging report (also called an AR aging report) helps your business identify, track, and manage your open invoices.
- Consider your typical payment terms—net-30, net-60, or something else—to determine the best time to generate your report for the most accurate snapshot.
- By categorizing invoices, businesses can quickly see which accounts are at risk and require immediate attention.
- For SaaS businesses with recurring revenue, understanding these patterns is especially important for accurate forecasting and strategic planning.
Double Entry Bookkeeping
At the end of an accounting period, the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts reduces the Accounts Receivable to produce Net Accounts Receivable. Note that allowance for doubtful accounts reduces the overall accounts receivable account, not a specific accounts receivable assigned to a customer. Because it is an estimation, it means the exact account that is (or will become) uncollectible is not yet known. For example, a customer takes out a $15,000 car loan on August 1, 2018 and is expected to pay the amount in full before December 1, 2018. For the sake of this example, assume that there was no interest charged to the buyer because of the short-term nature or life of the loan.

Document this process clearly so everyone on your team understands how and when to access these reports. Accounts Receivables aging is used to reflect a company’s ability to recover its credit sales in a certain accounting period. If the average age of accounts receivables is large, its ability to recover credit sales is worse. Under the Aging of Accounts Receivable Method, the estimate accounting is updated at the end of each accounting period so it is based on the most recent Accounts Receivable Aging Report. The following examples show the journal entries when the account has a zero balance, a credit balance, or a debit balance.


